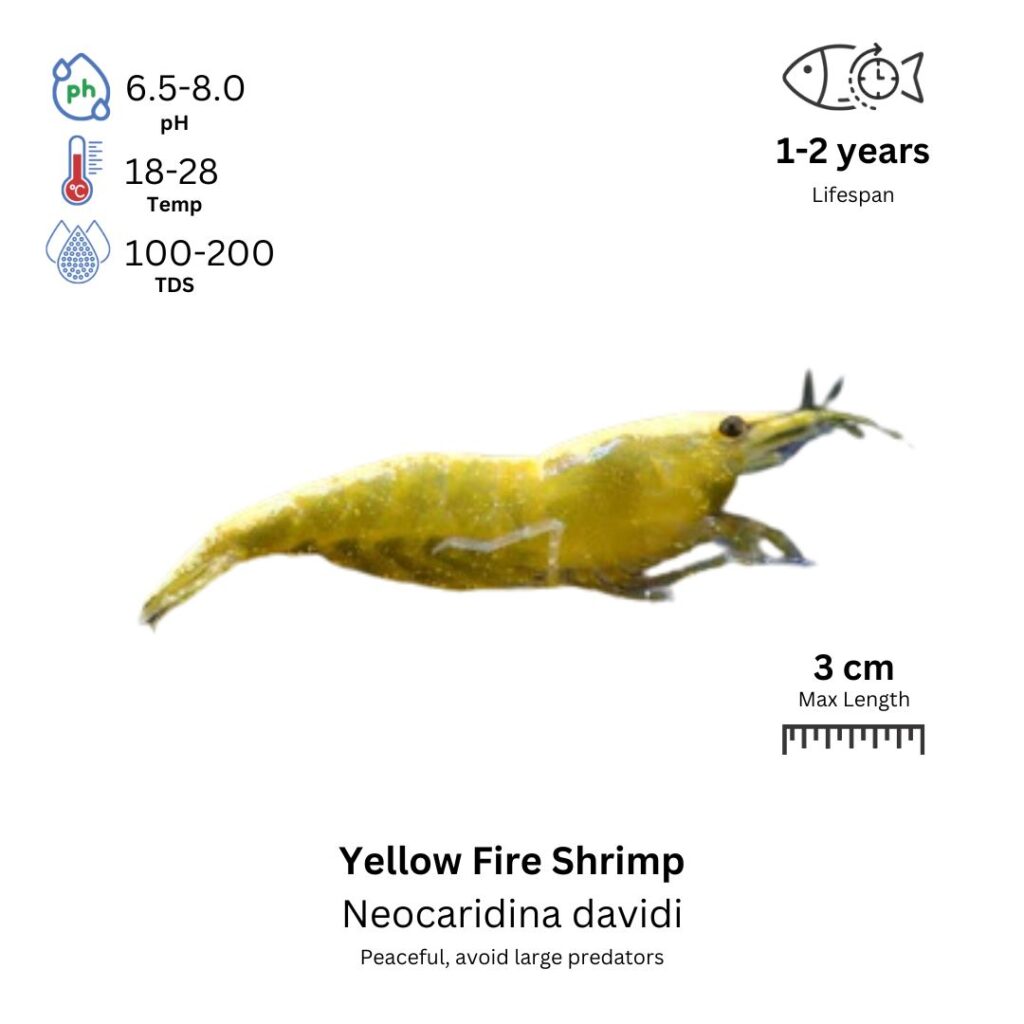
Yellow Fire Shrimp
Caridina cf. cantonensis

Description
The Yellow Fire Shrimp is a striking, vibrant freshwater shrimp known for its bright yellow coloration, which can range from pale yellow to deep gold. This shrimp has a slender, translucent body adorned with a bright yellow hue that covers most of its exoskeleton. It also features distinctive black markings along its body, including a black line running along its back and a dark spot near its tail, giving it a fiery appearance. Yellow Fire Shrimp are peaceful, active, and excellent scavengers, often seen cleaning algae and detritus from rocks, plants, and tank surfaces. They are also known for their interesting behavior, frequently seen molting and grooming themselves.
Habitat Origin
Native to freshwater environments in Southeast Asia, particularly from Taiwan, where they live in clean, well-oxygenated streams and rivers with dense vegetation and soft substrates.
Aquarium
Ideal Number in Aquarium: At least 5-6 individuals, as they are social creatures and feel more secure in groups.
Favorite Food
Yellow Fire Shrimp are omnivores and will consume a variety of foods, including algae, biofilm, detritus, and leftover fish food. They can also be supplemented with high-quality shrimp pellets, blanched vegetables (like zucchini and spinach), and small amounts of protein such as daphnia or brine shrimp. A varied diet will ensure they maintain their vibrant color and overall health.
Behavior:
Yellow Fire Shrimp are peaceful and active, often seen foraging and grazing on the tank’s surfaces for food. They are relatively shy and may retreat to hiding spots like plants or rocks when they feel threatened. These shrimp are also known for their grooming behavior, often seen picking at their legs or cleaning themselves. They are not aggressive and generally live harmoniously with other peaceful fish and invertebrates. They can sometimes be observed interacting with tankmates, particularly smaller, peaceful species.
Special Care:
These shrimp require a stable, well-maintained environment with clean, slightly acidic water. A well-planted tank with plenty of hiding spots is ideal, as it provides them with the security they need. Yellow Fire Shrimp are sensitive to copper, so any copper-based medications should be avoided in the tank. Additionally, they thrive in tanks with stable water parameters, so regular water changes and proper filtration are essential. The shrimp also require a source of calcium to help with molting, so adding calcium supplements (like cuttlebone or shrimp-specific mineral blocks) can be beneficial.
Compatibility with Other Fish:
Yellow Fire Shrimp are peaceful and can be kept with other small, non-aggressive fish such as tetras, rasboras, and other shrimp species. However, they should be kept with fish that won’t disturb them or nip at their delicate antennae and legs. Larger or more aggressive fish, particularly those that hunt invertebrates, should be avoided. They are also safe with peaceful bottom-dwellers like Corydoras or small catfish.
Breeding Tank Setup
Yellow Fire Shrimp adalah salah satu varietas warna cerah dari Neocaridina davidi dan merupakan salah satu udang hias paling mudah dibreeding di akuarium rumah, bahkan oleh pemula. Siapkan akuarium minimal 10–20 liter dengan filter spons dan substrat halus seperti pasir atau tanah liat bakar. Tambahkan tanaman hidup seperti Java moss, Bucephalandra, atau riccia sebagai tempat berlindung dan area biofilm alami untuk burayak. Parameter air ideal meliputi pH 6,5–7,5, suhu 22–26°C, dan kekerasan rendah hingga sedang (4–8 dGH, 6–10 KH). Hindari penggunaan tembaga dalam media filtrasi atau obat, karena bersifat mematikan bagi udang.
Conditioning for Breeding
To prepare shrimp for breeding, provide a nutritious and balanced diet. Feed them high-quality shrimp pellets, blanched vegetables (e.g., zucchini, spinach, carrots), and occasional live foods like brine shrimp or daphnia. This enhances egg production and overall health. Conduct weekly water changes of 20–30%. To stimulate spawning, perform a larger 50% water change and raise the temperature to 28°C, mimicking rainy season conditions that naturally trigger breeding.
Spawning Behavior
Spawning can occur year-round under stable, clean conditions. Females molt and release pheromones; males respond by searching for them. Fertilized eggs are carried under the female’s abdomen for 3–4 weeks. A healthy female can carry 30–40 eggs per cycle. Unlike many fish, adults do not eat their offspring, so separation is unnecessary. However, good water quality is vital during this period to ensure successful hatching and fry development.
Fry Development & Feeding
The eggs hatch directly into miniature shrimp after 3–4 weeks, bypassing a larval stage. Fry start foraging immediately and should be provided with infusoria, liquid fry food, and later baby brine shrimp or microworms. They also feed on biofilm and algae present in the tank. Maintain water cleanliness with daily or alternate-day 10–20% water changes, ensure temperature remains 22–28°C, and avoid overfeeding, as poor water quality is the biggest threat to survival.
Additional Notes for Success
Yellow Fire Shrimp reach sexual maturity at 3–4 months. Females are larger with rounder abdomens, especially when berried (carrying eggs), while males are slimmer and more active during courtship. Avoid stress by maintaining stable parameters and keeping the tank free of aggressive tank mates or overcrowding. A peaceful, well-planted, and biofilm-rich environment leads to a self-sustaining breeding colony over time.